Smart Railways Market Synopsis
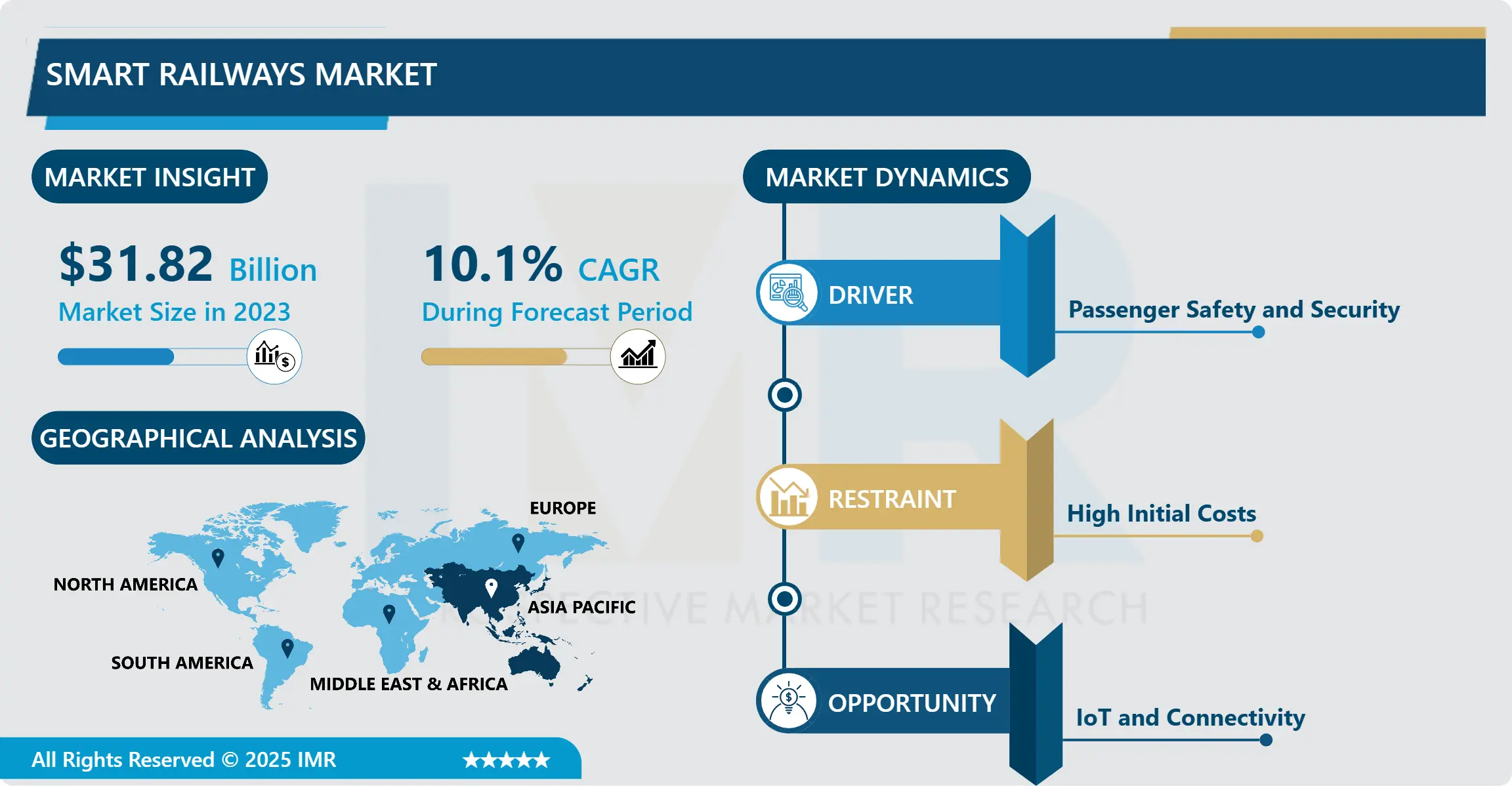
Smart Railways Market Size Was Valued at USD 31.82 Billion in 2023, and is Projected to Reach USD 75.65 Billion by 2032, Growing at a CAGR of 10.10% From 2024-2032.
The term "Smart Railways" refers to the integration of advanced technologies and digital solutions within the railway infrastructure and operations to enhance safety, efficiency, and passenger experience. This includes the deployment of IoT (Internet of Things) sensors for real-time monitoring of trains, tracks, and infrastructure, leveraging big data analytics to optimize scheduling and maintenance, implementing automated ticketing and passenger information systems, and adopting communication technologies like 5G for reliable connectivity. Smart Railways aim to improve operational performance, reduce costs, minimize environmental impact, and offer passengers seamless and enhanced travel experiences through the application of innovative technologies.
The global smart railways market is witnessing significant growth driven by the convergence of digital technologies with traditional railway systems, aimed at revolutionizing transportation efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Smart railways leverage advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and communication networks to optimize operations, enhance passenger experience, and ensure operational safety.
One of the primary drivers of this market growth is the increasing urbanization and population density in major cities worldwide, which necessitates efficient and reliable transportation solutions. Smart railways address these demands by offering predictive maintenance capabilities, real-time monitoring of assets, and automated train control systems that minimize delays and improve service reliability. These technologies also enable railways to optimize energy consumption, reduce carbon footprints, and enhance overall environmental sustainability.
Moreover, government initiatives promoting smart city development and infrastructure modernization projects are further fueling market expansion. Investments in upgrading rail infrastructure, deploying intelligent signaling systems, and integrating smart ticketing solutions are enhancing the overall efficiency of rail networks globally.
However, the adoption of smart railways faces challenges such as high initial costs of implementing advanced technologies and the interoperability issues between existing legacy systems and new digital solutions. Overcoming these challenges requires substantial investments in research and development, along with collaborative efforts among stakeholders across the railway ecosystem.
Looking ahead, the smart railways market is poised for continued growth, driven by ongoing technological innovations and partnerships aimed at addressing industry challenges. The focus remains on improving operational efficiency, enhancing passenger safety, and meeting the growing demands for sustainable urban transportation solutions in an increasingly interconnected world.

Smart Railways Market Trend Analysis
Predictive Maintenance Solutions in the Smart Railways Market
- Predictive maintenance solutions have emerged as a transformative trend in the smart railways sector, leveraging IoT sensors and advanced predictive analytics to revolutionize maintenance practices. These solutions enable continuous monitoring of critical components such as tracks, rolling stock, and signaling systems in real-time. By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data, operators can detect potential faults or anomalies before they escalate into costly failures.
- The implementation of IoT sensors throughout railway infrastructure provides a wealth of data on factors like temperature, vibration, and performance metrics. This data is then processed using sophisticated algorithms that predict maintenance needs based on patterns and deviations from normal operating conditions. By proactively addressing maintenance issues, operators can schedule repairs during off-peak hours or downtime periods, minimizing disruption to passenger services and freight operations.
- Furthermore, predictive maintenance not only enhances reliability but also improves safety by reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns or malfunctions. It allows railway operators to move from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies, optimizing asset utilization and extending the lifespan of critical infrastructure. As smart railways continue to evolve, predictive maintenance solutions will play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and sustainable transportation networks worldwide.
Implementation of Smart Signaling Systems in the Smart Railways Market
- The implementation of smart signaling systems, such as ETCS and CBTC, marks a significant advancement in the smart railways sector, aimed at improving operational efficiency and safety. ETCS, known as the European Train Control System, standardizes signaling and control across Europe, replacing traditional signaling systems with a unified, digital interface. This system uses continuous communication between trains and trackside equipment, enabling precise control of train movements based on real-time conditions. By providing accurate information on train positions, speeds, and routes, ETCS enhances traffic management, reduces congestion, and minimizes the risk of accidents caused by human error or miscommunication.
- Similarly, CBTC, or Communication-Based Train Control, represents a leap forward in signaling technology by enabling trains to communicate directly with control centers and each other. Unlike traditional fixed-block signaling, which divides tracks into segments with fixed safety margins, CBTC dynamically adjusts train separation based on actual train positions and speeds. This capability allows for higher train frequencies, increased capacity on existing infrastructure, and more efficient use of railway networks.
- Moreover, smart signaling systems contribute to improved safety by continuously monitoring train movements and automatically applying braking or speed restrictions when necessary. Real-time data feedback ensures that trains maintain safe distances and speeds, reducing the risk of collisions and derailments. As railway operators worldwide face increasing demands for reliable and safe transportation services, smart signaling systems like ETCS and CBTC are crucial in modernizing infrastructure and meeting the challenges of growing urbanization and passenger volumes. Their adoption not only enhances operational efficiency but also sets a foundation for future smart railway developments aimed at sustainable and resilient transport systems.
Smart Railways Market Segment Analysis:
Smart Railways Market Segmented based on By Device and Component, By Service and By System.
By Device and Component, Rail Sensors segment is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period
- In today's railway operations, rail sensors are essential equipment that are used to monitor and maintain the health of the infrastructure. These sensors are positioned strategically inside rolling stock and along tracks to gather data in real-time on a variety of characteristics, including axle counts, temperature, and vibrations on the rails. Rail operators can avert future failures by recognizing anomalies early on and gaining useful insights into the health of the rails through continuous data collection and analysis. Predictive maintenance is a proactive approach to maintenance that lowers operating costs, minimizes downtime, and improves overall system reliability.
- The possibilities of rail sensors have been transformed by developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT facilitates real-time data transmission by enabling seamless connectivity between sensors and central monitoring systems. By analyzing this data, AI algorithms can forecast probable malfunctions or the need for repair, which helps to optimize resource allocation and maintenance plans. Furthermore, the accuracy of defect diagnosis and detection is improved by AI-powered analytics, allowing for prompt interventions and proactive decision-making. By ensuring that train systems run at optimal performance levels with no interruption, this IoT and AI integration greatly enhances operational efficiency and increases passenger safety.
- The crucial role that rail sensors play in maintaining operational integrity and passenger safety is shown by their incorporation into larger railway systems. Apart from anticipatory maintenance, these sensors facilitate other operational facets like traffic control, planning, and energy conservation. For example, computerized traffic control systems can improve rail operations and lessen congestion by using sensors to monitor train positions and speeds. Environmental sensors also support efforts to reduce environmental impact and improve passenger comfort by monitoring noise levels and air quality around train stops. Rail sensors will be at the forefront of technologies that improve the sustainability and efficiency of railway transportation networks globally as smart railway efforts continue to develop.
By System, Passenger Information Systems (PIS) segment held the largest share in 2023
- Professional services are essential pillars in the deployment, maintenance, and optimization of smart railway systems, offering specialized expertise and support throughout the lifecycle of railway projects. Consulting services play a foundational role by providing strategic guidance and feasibility assessments at the project inception stage. Consultants collaborate closely with railway authorities and operators to define project goals, assess technological requirements, and develop comprehensive implementation strategies. This early involvement helps align smart railway initiatives with broader organizational objectives while ensuring feasibility and scalability.
- Project management is another critical component of professional services within smart railways, focusing on overseeing project execution, resource allocation, and timeline adherence. Experienced project managers leverage industry best practices to streamline workflows, mitigate risks, and optimize project outcomes. By implementing robust project management methodologies, such as Agile or Waterfall, these professionals facilitate effective communication across project teams and stakeholders, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the project lifecycle.
- Technical support forms the backbone of ongoing maintenance and operational support for smart railway systems. Technical experts provide troubleshooting assistance, software updates, and system enhancements to optimize performance and address evolving operational needs. Their proactive approach to maintenance helps minimize downtime, improve system reliability, and maximize the return on investment in smart railway technologies. Moreover, continuous technical support ensures that railway operators can leverage the full capabilities of their systems, integrating new technologies seamlessly and adapting to changing operational environments.
- Overall, professional services in smart railways not only ensure the successful deployment of advanced technologies but also contribute significantly to enhancing operational efficiency and passenger satisfaction. By offering comprehensive consulting, project management, and technical support services, professionals in this field play a pivotal role in driving innovation and facilitating the seamless integration of smart railway technologies into existing infrastructures. As railway networks continue to evolve and expand globally, the demand for specialized professional services is expected to grow, further emphasizing their indispensable role in shaping the future of railway transportation.
Smart Railways Market Regional Insights:
Asia Pacific is Expected to Dominate the Market Over the Forecast period
- Asia Pacific is becoming a major player in the smart railways industry thanks to a number of important growth-promoting elements. The swift urbanization of nations such as China, India, and Japan has resulted in a surge in the need for effective and environmentally friendly transportation options. To accommodate the growing urban population and relieve pressure on the current transportation infrastructure, the governments of these countries are making large investments in high-speed rail networks. China, for example, has the greatest high-speed rail network in the world, and it serves as an example of the region's dedication to improving connectivity and cutting down on travel times between key cities.
- Additionally, investments in automated train operations and smart signaling systems are being driven by growing mobility needs and a move toward environmentally friendly modes of transportation. These technologies increase safety and dependability throughout rail networks in addition to operational efficiency. Japan is well known for being at the forefront of railway technology innovation. The country continues to set the standard for the area by implementing cutting-edge systems like automated ticketing, real-time passenger information, and predictive maintenance.
- Moreover, the modernization of the transport infrastructure in Asia Pacific is mostly dependent on government initiatives. The implementation of semi-high-speed trains and the construction of dedicated freight corridors in India are examples of initiatives to update antiquated rail networks and incorporate contemporary technology for increased sustainability and efficiency. By encouraging cleaner forms of transportation, such programs not only address environmental problems but also accelerate economic growth.
- With strategic investments, technical developments, and a proactive approach to serving the changing transportation needs of a rapidly urbanizing population, the smart railroads market in Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a strong rate overall. The region is anticipated to continue serving as a key center for innovation and growth in the global railway sector as these countries build out their networks and improve their operational capacities.
Active Key Players in the Smart Railways Market
- ABB Group
- General Electric
- Huawei Technologies
- Hitachi
- Cisco Systems
- Siemens
- IBM Corporation
- Indra Sistemas
- Alstom
- Alcatel-Lucent
- Bombardier
- Ansaldo STS
- Capgemini
- Nokia
- Other Key Players
Key Industry Developments in the Smart Railways Market:
- November 2023 - Siemens Mobility introduced its latest stock product with its first electric Mireo Smart train at the rail technology company's factory in Krefeld, Germany. The new train, mainly built for regional and commuter rail operators, is crucial to the company's attempts to capitalize on demand for more sustainable rolling stock solutions.
- June 2023 - Huawei Technologies launched four Intelligent OptiX innovative practices of F5.5G in scenarios of smart homes, small and micro enterprises, smart manufacturing, and metro networks. Using the company's Alps-WDM, China Unicom Chongqing has built metro networks with the optimal TCO. Huawei's Alps-WDM increased the single-wavelength rate from 10G to 100G at the integrated access site.
|
Smart Railways Market |
|||
|
Base Year: |
2023 |
Forecast Period: |
2024-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2017 to 2023 |
Market Size in 2023: |
USD 31.82 Bn. |
|
Forecast Period 2024-32 CAGR: |
10.10% |
Market Size in 2032: |
USD 75.65 Bn. |
|
Segments Covered: |
By Device and Component |
|
|
|
By Service |
|
||
|
By System |
|
||
|
By Region |
|
||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
|
||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
|
||
|
Key Opportunities: |
|
||
|
Companies Covered in the report: |
ABB Group, General Electric, Huawei Technologies, Hitachi Cisco Systems, Siemens, IBM Corporation, Indra Sistemas Alstom, Alcatel-Lucent, Bombardier, Ansaldo STS, Capgemini, Nokia, and Other Major Players. |
||
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Scope and Coverage
Chapter 2:Executive Summary
Chapter 3: Market Landscape
3.1 Market Dynamics
3.1.1 Drivers
3.1.2 Restraints
3.1.3 Opportunities
3.1.4 Challenges
3.2 Market Trend Analysis
3.3 PESTLE Analysis
3.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
3.5 Industry Value Chain Analysis
3.6 Ecosystem
3.7 Regulatory Landscape
3.8 Price Trend Analysis
3.9 Patent Analysis
3.10 Technology Evolution
3.11 Investment Pockets
3.12 Import-Export Analysis
Chapter 4: Smart Railways Market by Device and Component (2018-2032)
4.1 Smart Railways Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
4.2 Market Overview
4.3 Rail Sensors
4.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
4.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
4.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
4.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
4.4 Video Surveillance Cameras
4.5 Smart Cards
4.6 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
4.7 Wi-Fi
4.8 Switches
4.9 etc.)
4.10 Others (Multimedia Displays)
Chapter 5: Smart Railways Market by Service (2018-2032)
5.1 Smart Railways Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
5.2 Market Overview
5.3 Professional Services
5.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
5.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
5.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
5.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
5.4 Cloud Services
5.5 Integration Services
Chapter 6: Smart Railways Market by System (2018-2032)
6.1 Smart Railways Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
6.2 Market Overview
6.3 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
6.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
6.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
6.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
6.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
6.4 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
6.5 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
6.6 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
6.7 Rail Operations Management Systems
6.8 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
6.9 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
Chapter 7: Company Profiles and Competitive Analysis
7.1 Competitive Landscape
7.1.1 Competitive Benchmarking
7.1.2 Smart Railways Market Share by Manufacturer (2024)
7.1.3 Industry BCG Matrix
7.1.4 Heat Map Analysis
7.1.5 Mergers and Acquisitions
7.2 ABB GROUP
7.2.1 Company Overview
7.2.2 Key Executives
7.2.3 Company Snapshot
7.2.4 Role of the Company in the Market
7.2.5 Sustainability and Social Responsibility
7.2.6 Operating Business Segments
7.2.7 Product Portfolio
7.2.8 Business Performance
7.2.9 Key Strategic Moves and Recent Developments
7.2.10 SWOT Analysis
7.3 GENERAL ELECTRIC
7.4 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES
7.5 HITACHI
7.6 CISCO SYSTEMS
7.7 SIEMENS
7.8 IBM CORPORATION
7.9 INDRA SISTEMAS
7.10 ALSTOM
7.11 ALCATEL-LUCENT
7.12 BOMBARDIER
7.13 ANSALDO STS
7.14 CAPGEMINI
7.15 NOKIA
7.16 OTHER KEY PLAYERS
Chapter 8: Global Smart Railways Market By Region
8.1 Overview
8.2. North America Smart Railways Market
8.2.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.2.2 Top Key Companies
8.2.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.2.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Device and Component
8.2.4.1 Rail Sensors
8.2.4.2 Video Surveillance Cameras
8.2.4.3 Smart Cards
8.2.4.4 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
8.2.4.5 Wi-Fi
8.2.4.6 Switches
8.2.4.7 etc.)
8.2.4.8 Others (Multimedia Displays)
8.2.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Service
8.2.5.1 Professional Services
8.2.5.2 Cloud Services
8.2.5.3 Integration Services
8.2.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by System
8.2.6.1 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
8.2.6.2 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
8.2.6.3 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
8.2.6.4 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
8.2.6.5 Rail Operations Management Systems
8.2.6.6 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
8.2.6.7 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
8.2.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.2.7.1 US
8.2.7.2 Canada
8.2.7.3 Mexico
8.3. Eastern Europe Smart Railways Market
8.3.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.3.2 Top Key Companies
8.3.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.3.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Device and Component
8.3.4.1 Rail Sensors
8.3.4.2 Video Surveillance Cameras
8.3.4.3 Smart Cards
8.3.4.4 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
8.3.4.5 Wi-Fi
8.3.4.6 Switches
8.3.4.7 etc.)
8.3.4.8 Others (Multimedia Displays)
8.3.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Service
8.3.5.1 Professional Services
8.3.5.2 Cloud Services
8.3.5.3 Integration Services
8.3.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by System
8.3.6.1 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
8.3.6.2 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
8.3.6.3 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
8.3.6.4 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
8.3.6.5 Rail Operations Management Systems
8.3.6.6 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
8.3.6.7 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
8.3.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.3.7.1 Russia
8.3.7.2 Bulgaria
8.3.7.3 The Czech Republic
8.3.7.4 Hungary
8.3.7.5 Poland
8.3.7.6 Romania
8.3.7.7 Rest of Eastern Europe
8.4. Western Europe Smart Railways Market
8.4.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.4.2 Top Key Companies
8.4.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.4.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Device and Component
8.4.4.1 Rail Sensors
8.4.4.2 Video Surveillance Cameras
8.4.4.3 Smart Cards
8.4.4.4 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
8.4.4.5 Wi-Fi
8.4.4.6 Switches
8.4.4.7 etc.)
8.4.4.8 Others (Multimedia Displays)
8.4.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Service
8.4.5.1 Professional Services
8.4.5.2 Cloud Services
8.4.5.3 Integration Services
8.4.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by System
8.4.6.1 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
8.4.6.2 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
8.4.6.3 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
8.4.6.4 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
8.4.6.5 Rail Operations Management Systems
8.4.6.6 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
8.4.6.7 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
8.4.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.4.7.1 Germany
8.4.7.2 UK
8.4.7.3 France
8.4.7.4 The Netherlands
8.4.7.5 Italy
8.4.7.6 Spain
8.4.7.7 Rest of Western Europe
8.5. Asia Pacific Smart Railways Market
8.5.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.5.2 Top Key Companies
8.5.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.5.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Device and Component
8.5.4.1 Rail Sensors
8.5.4.2 Video Surveillance Cameras
8.5.4.3 Smart Cards
8.5.4.4 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
8.5.4.5 Wi-Fi
8.5.4.6 Switches
8.5.4.7 etc.)
8.5.4.8 Others (Multimedia Displays)
8.5.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Service
8.5.5.1 Professional Services
8.5.5.2 Cloud Services
8.5.5.3 Integration Services
8.5.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by System
8.5.6.1 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
8.5.6.2 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
8.5.6.3 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
8.5.6.4 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
8.5.6.5 Rail Operations Management Systems
8.5.6.6 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
8.5.6.7 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
8.5.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.5.7.1 China
8.5.7.2 India
8.5.7.3 Japan
8.5.7.4 South Korea
8.5.7.5 Malaysia
8.5.7.6 Thailand
8.5.7.7 Vietnam
8.5.7.8 The Philippines
8.5.7.9 Australia
8.5.7.10 New Zealand
8.5.7.11 Rest of APAC
8.6. Middle East & Africa Smart Railways Market
8.6.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.6.2 Top Key Companies
8.6.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.6.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Device and Component
8.6.4.1 Rail Sensors
8.6.4.2 Video Surveillance Cameras
8.6.4.3 Smart Cards
8.6.4.4 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
8.6.4.5 Wi-Fi
8.6.4.6 Switches
8.6.4.7 etc.)
8.6.4.8 Others (Multimedia Displays)
8.6.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Service
8.6.5.1 Professional Services
8.6.5.2 Cloud Services
8.6.5.3 Integration Services
8.6.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by System
8.6.6.1 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
8.6.6.2 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
8.6.6.3 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
8.6.6.4 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
8.6.6.5 Rail Operations Management Systems
8.6.6.6 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
8.6.6.7 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
8.6.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.6.7.1 Turkiye
8.6.7.2 Bahrain
8.6.7.3 Kuwait
8.6.7.4 Saudi Arabia
8.6.7.5 Qatar
8.6.7.6 UAE
8.6.7.7 Israel
8.6.7.8 South Africa
8.7. South America Smart Railways Market
8.7.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.7.2 Top Key Companies
8.7.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.7.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Device and Component
8.7.4.1 Rail Sensors
8.7.4.2 Video Surveillance Cameras
8.7.4.3 Smart Cards
8.7.4.4 Networking & Connectivity Devices (Router
8.7.4.5 Wi-Fi
8.7.4.6 Switches
8.7.4.7 etc.)
8.7.4.8 Others (Multimedia Displays)
8.7.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Service
8.7.5.1 Professional Services
8.7.5.2 Cloud Services
8.7.5.3 Integration Services
8.7.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by System
8.7.6.1 Passenger Information Systems (PIS)
8.7.6.2 Railway Traffic Management System (RTMS)
8.7.6.3 Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS)
8.7.6.4 Smart Ticketing Systems (STS)
8.7.6.5 Rail Operations Management Systems
8.7.6.6 Rail Communication & Networking Systems
8.7.6.7 Others (Rail Analytics Systems and Freight Information Systems)
8.7.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.7.7.1 Brazil
8.7.7.2 Argentina
8.7.7.3 Rest of SA
Chapter 9 Analyst Viewpoint and Conclusion
9.1 Recommendations and Concluding Analysis
9.2 Potential Market Strategies
Chapter 10 Research Methodology
10.1 Research Process
10.2 Primary Research
10.3 Secondary Research
|
Smart Railways Market |
|||
|
Base Year: |
2023 |
Forecast Period: |
2024-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2017 to 2023 |
Market Size in 2023: |
USD 31.82 Bn. |
|
Forecast Period 2024-32 CAGR: |
10.10% |
Market Size in 2032: |
USD 75.65 Bn. |
|
Segments Covered: |
By Device and Component |
|
|
|
By Service |
|
||
|
By System |
|
||
|
By Region |
|
||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
|
||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
|
||
|
Key Opportunities: |
|
||
|
Companies Covered in the report: |
ABB Group, General Electric, Huawei Technologies, Hitachi Cisco Systems, Siemens, IBM Corporation, Indra Sistemas Alstom, Alcatel-Lucent, Bombardier, Ansaldo STS, Capgemini, Nokia, and Other Major Players. |
||













