LNG Market Synopsis
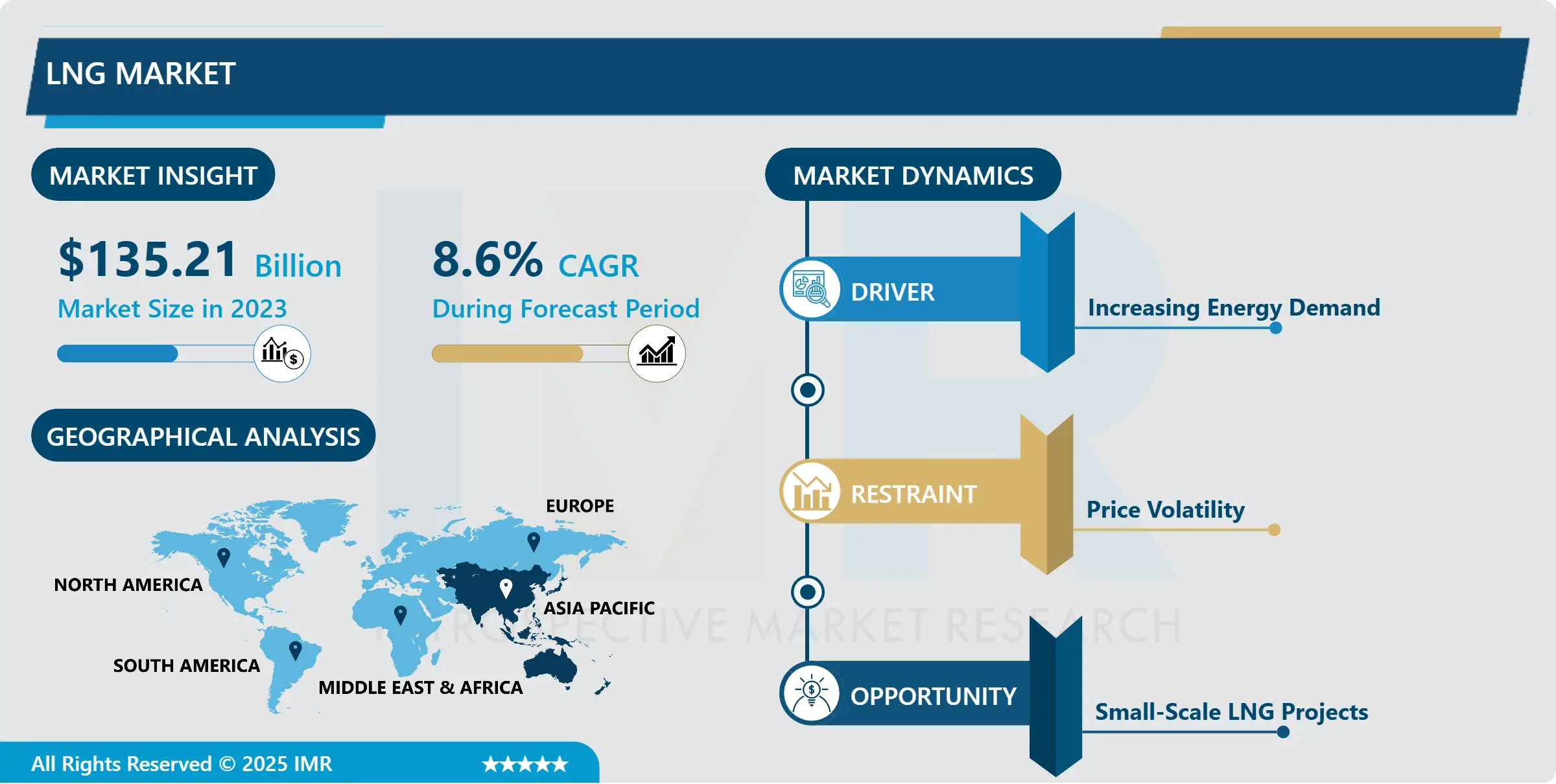
The global LNG Market was valued at USD 146.84 billion in 2024 and is likely to reach USD 284.10 billion by 2032, increasing at a CAGR of 8.6% from 2025 to 2032.
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is characteristic gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with a few blends of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to fluid form for ease and security of non-pressurized capacity or transport.
It takes up approximately 1/600th the volume of characteristic gas within the vaporous state at standard conditions for temperature and weight. The LNG market is not – nor will it ever be – as flexible as the world oil market. The high costs of LNG transportation still make it difficult to move the commodity physically over long distances. Only when there is surplus capacity in liquefaction plants and tankers can LNG compete in distant markets. And in those cases it competes on a marginal cost basis where the investor recovers less than his originally planned return on investment. Nor is LNG likely to achieve the competitive commodity status that the liberalised gas markets of North America, the UK and increasingly the Continent have produced. The longterm contract in LNG has been the vehicle for sharing the large up-front investment risks that characterise LNG projects.
The short-term LNG market, while growing, still remains at less than 9% of total trade. But more significantly, no new LNG train has been launched without at least some long-term contract coverage. Thus it appears that the long-term contract in LNG will remain a mainstay of international LNG trade even if it has all but disappeared in onshore North America. The concept of using financial derivatives to manage risk on these multi-billion-dollar projects is probably unrealistic.
In large ocean shipments, LNG is loaded onto double-bottom vessels, which are used for both safety and isolation purposes. When the ship arrives at the receiving port, the LNG is unloaded in well-insulated tanks and then regasified to enter the pipeline distribution network. LNG can also be delivered in smaller quantities, usually for shorter sea voyages. Business of small-volume LNG vessels is growing and they are mostly made of the same containers used in trucks and international trade, specially equipped with cryogenic tanks.
Other small-scale LNG operations include "peak-razor" liquefaction and storage facilities that can hold gas when it is needed during periods of peak demand in local US markets. Sometimes LNG is also imported or exported from such a facility by truck. In 2020, the United States exported nearly 2.4 trillion cubic feet (Bcf) of natural gas as LNG via large LNG carriers and small amounts by container or truck. In total, US LNG was delivered to 40 countries on five continents by August 2021. The US also continues to import LNG, mostly to New England, a region of the country constrained by limited pipelines and storage capacity.

LNG Market Trend Analysis
LNG Market Growth Drivers- Increasing Energy Demand
- Rising economies, especially in regions such as Asia, Africa, and Latin America, are encountering quick financial development and industrialization. This development requires significant increases in energy consumption to control businesses, infrastructure, and urban advancement. As nations like China, India, and different African countries extend their fabricating capabilities and urban centers, the request for dependable and proficient energy sources surges.
- Urbanization is another critical factor contributing to expanded energy demand. As more individuals move to urban regions in look of better opportunities and living standards, the energy required for lodging, transportation, and open administrations develops exponentially. Urban centers require steady and adaptable energy supplies to preserve financial exercises and give for their populations. Numerous rising economies are too encountering noteworthy populace development. A bigger population inherently requires more energy for residential use, commercial activities, and public infrastructure.
- This statistic move puts extra weight on existing energy resources and makes a pressing require for feasible and adaptable energy solutions. As the standard of living improves in these regions, there's the next request for energy-intensive merchandise and administrations, such as discuss conditioning, warming, family machines, and electronic gadgets. The expanded utilization of these merchandise and administrations leads to more noteworthy by and large vitality utilization. Rising economies are progressively centered on guaranteeing vitality security and expanding their vitality sources.
- Dependence on a single vitality source or on vitality imports from politically unsteady locales can posture dangers. LNG gives an elective that can be sourced from different districts around the world, diminishing reliance and improving vitality security. Compared to coal and oil, LNG could be a cleaner fossil fuel, creating lower levels of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, as well as essentially less carbon dioxide. As worldwide and national arrangements thrust for cleaner energy solutions to combat discuss pollution and climate change, LNG becomes a more attractive choice. This is often especially important in nations confronting serious air quality issues due to dependence on coal-fired power plants.
LNG Market Opportunities- Small-Scale LNG Projects
- The development of small-scale Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) projects is progressively recognized as a key approach to extend market reach, especially in inaccessible and underserved zones. These ventures center on creating, transporting, and utilizing LNG in smaller amounts compared to conventional large-scale operations, advertising a run of benefits and openings. Small-scale LNG projects are inalienably more adaptable and scalable than large-scale operations. They can be custom-made to meet the particular energy needs of neighbourhood or regional markets, permitting for more exact matching of supply and demand. This adaptability is pivotal for regions where energy necessities may not legitimize the speculation in large-scale foundation.
- One of the foremost critical advantages of small-scale LNG is its capacity to reach farther and confined ranges that need get to to conventional energy sources such as common gas pipelines or reliable power grids. These regions frequently depend on exorbitant and naturally hurtful fills like diesel. Small-scale LNG gives a cleaner and more cost-effective elective, progressing energy get to and supporting local development. Compared to large-scale LNG projects, small-scale activities require lower capital investment. The reduced monetary burden makes it attainable for smaller substances, counting territorial governments, neighborhood utilities, and private endeavors, to contribute in and advantage from LNG.
- This lower venture edge can quicken the appropriation of LNG in different districts. Small-scale LNG ventures ordinarily have shorter advancement timelines due to their smaller measure and less complex framework requirements. This empowers speedier arrangement and faster realization of benefits. For communities and businesses in require of prompt energy solutions, small-scale LNG can give a opportune and compelling reaction. By setting up small-scale LNG ventures, nearby economies can advantage through work creation, aptitudes improvement, and expanded financial action. Neighbourhood businesses can take an interest within the supply chain, and communities can experience improved energy security and quality of life. These ventures can act as catalysts for broader financial development and advancement. Small-scale LNG ventures contribute to environmental sustainability by replacing more contaminating fills such as coal, oil, and diesel. LNG produces lower emissions of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, as well as essentially less carbon dioxide. This move to cleaner vitality sources makes a difference moderate nearby discuss contamination and bolsters worldwide endeavours to combat climate change.
LNG Market Segment Analysis:
Market Segmented based on Nature, by LNG infrastructure, by Application, and region.
By Nature, Non-toxic Is Expected to Dominate the Market During the Forecast Period
By Nature segmented as Odourless, Colourless, Non-Toxic, Non-Corrosive
- The non-toxic nature of LNG makes it more secure to handle compared to other hydrocarbons. In case of a spill or leak, LNG does not posture the same wellbeing dangers as substances that are toxic. This reduces the potential for harm to people and the environment, making it a more alluring choice for different applications. LNG is considered a cleaner fossil fuel since it produces less pollutants and greenhouse gasses compared to coal and oil. The non-toxic property implies that within the event of a discharge, LNG will evaporate rapidly and does not take off behind harmful residues, which mitigates its natural affect.
- The non-toxic nature of LNG makes a difference in assembly stringent regulatory requirements forced by governments and natural agencies. This encourages the endorsement and improvement of LNG projects, contributing to market development. The non-toxic characteristic bolsters the development of the LNG market into private and commercial sectors where security may be a essential concern. For occasion, LNG can be utilized for heating and cooking in homes, or as fuel for vehicles, without posturing noteworthy wellbeing dangers.
By LNG Infrastructure, LNG Liquefaction Plants held the largest share
By LNG Infrastructure segmented as LNG Liquefaction Plants, LNG Regasification Facilities, LNG Shipping
- LNG liquefaction plants are the beginning point of the LNG supply chain. These offices are capable for changing over common gas into a fluid shape, which decreases its volume by around 600 times, making it attainable to transport huge amounts over long separations. Without liquefaction, the whole LNG industry would not exist, as transporting common gas in its vaporous state over such separations would be financially and actually unfeasible. Liquefaction plants require critical capital venture and progressed innovation. They include complex forms such as gas decontamination, parchedness, and cooling to cryogenic temperatures. This makes them basic and central to the LNG framework, frequently speaking to the largest financial and specialized jump within the LNG esteem chain.
- The area and capacity of liquefaction plants frequently direct the worldwide LNG supply flow. Nations with significant common gas saves contribute intensely in liquefaction offices to send out LNG, affecting worldwide vitality markets. The nearness of these plants positions these nations as key players within the LNG industry. Liquefaction plants have a considerable financial affect, frequently creating critical work openings and contributing to the neighborhood and national economy through sends out. They are more often than not seen as strategic national resources.
LNG Market Regional Insights:
Asia Pacific Region is Expected to Dominate the Market Over the Forecast Period
- Numerous nations within the Asia-Pacific locale, such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea, are encountering rapid economic growth and industrialization. This development is driving expanded energy demand, counting natural gas, to control businesses, businesses, and households. The Asia-Pacific region is domestic to a noteworthy parcel of the world's populace. As populaces develop and urbanization increments, the request for vitality, especially cleaner-burning powers like normal gas, is anticipated to rise significantly. With expanding mindfulness of natural issues and a developing accentuation on reducing greenhouse gas outflows, nations within the Asia-Pacific region are progressively turning to natural gas as a cleaner elective to coal and oil for control era, industrial processes, and transportation. Numerous governments within the Asia-Pacific region are executing arrangements and activities to advance the utilize of normal gas and diminish dependence on more contaminating fills. These policies incorporate motivations for LNG foundation advancement, ventures in cleaner energy technologies, and regulations aimed at reducing air pollution.
- The Asia-Pacific locale is contributing intensely in LNG infrastructure, counting liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, and pipelines, to meet growing demand. This infrastructure development is supported by both public and private sector investments and is fundamental for encouraging the moment, capacity, and distribution of LNG over the region. Nations within the Asia-Pacific locale are shaping strategic organizations and alliances to secure long-term LNG supplies. These associations include agreements for the advancement of LNG projects, long-term supply contracts, and ventures in LNG infrastructure, guaranteeing a steady and dependable supply of characteristic gas to meet developing demand.
LNG Market Top Key Players:
The top key companies in the LNG Market are:
- Qatar Petroleum (QP) (Qatar)
- Royal Dutch Shell (Netherlands/UK)
- ExxonMobil (USA)
- Chevron (USA)
- TotalEnergies (France)
- BP (British Petroleum) (UK)
- PetroChina (China)
- CNOOC (China National Offshore Oil Corporation) (China)
- Cheniere Energy (USA)
- ConocoPhillips (USA)
- Petronas (Petroliam Nasional Berhad) (Malaysia)
- Gazprom (Russia)
- Novatek (Russia)
- Eni (Italy)
- Repsol (Spain)
- Woodside Petroleum (Australia)
- Santos Limited (Australia)
- Equinor (formerly Statoil) (Norway)
- Sempra Energy (USA)
- KOGAS (Korea Gas Corporation) (South Korea)
- Mitsubishi Corporation (Japan)
- Mitsui & Co., Ltd. (Japan)
- JERA (Japan)
- Indian Oil Corporation (IOCL) (India)
- Sonatrach (Algeria) and Other Active Players.
Key Industry Developments in the Market:
- In May 2024, Shell sees emerging Asian markets taking more of world's growing LNG supply; Shell expects its Australian supplies of liquefied natural gas (LNG) to help meet demand from emerging markets in south and southeast Asia, which are tipped to absorb some of the pickup in global supplies towards the end of this decade.
- In March 2023: Sempra reported that Sempra Infrastructure Partners LP (Sempra Infrastructure), its 70%-owned subsidiary, reached a positive final investment decision (FID) for the development, construction, and operation of the Port Arthur LNG Phase 1 project in Jefferson County, Texas.
|
Global LNG Market |
|||
|
Base Year: |
2024 |
Forecast Period: |
2025-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2018-2023 |
Market Size In 2024: |
USD 146.84 Billion |
|
Forecast Period 2024-32 CAGR: |
8.6% |
Market Size In 2032: |
USD 284.10 Billion |
|
Segments Covered: |
By Nature |
|
|
|
By LNG Infrastructure |
|
||
|
By Category |
|
||
|
By Region |
|
||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
|
||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
|
||
|
Key Opportunities: |
|
||
|
Companies Covered in The Report: |
|
||
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Scope and Coverage
Chapter 2:Executive Summary
Chapter 3: Market Landscape
3.1 Market Dynamics
3.1.1 Drivers
3.1.2 Restraints
3.1.3 Opportunities
3.1.4 Challenges
3.2 Market Trend Analysis
3.3 PESTLE Analysis
3.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
3.5 Industry Value Chain Analysis
3.6 Ecosystem
3.7 Regulatory Landscape
3.8 Price Trend Analysis
3.9 Patent Analysis
3.10 Technology Evolution
3.11 Investment Pockets
3.12 Import-Export Analysis
Chapter 4: LNG Market by Nature (2018-2032)
4.1 LNG Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
4.2 Market Overview
4.3 Odourless
4.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
4.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
4.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
4.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
4.4 Colourless
4.5 Non-Toxic
4.6 Non-Corrosive
Chapter 5: LNG Market by LNG Infrastructure (2018-2032)
5.1 LNG Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
5.2 Market Overview
5.3 LNG Liquefaction Plants
5.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
5.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
5.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
5.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
5.4 LNG Regasification Facilities
5.5 LNG Shipping
Chapter 6: LNG Market by Category (2018-2032)
6.1 LNG Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
6.2 Market Overview
6.3 Transportation
6.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
6.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
6.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
6.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
6.4 Household
6.5 LNG Trucks
6.6 LNG Bus
6.7 Train
6.8 Trade
6.9 Maritime Application
Chapter 7: Company Profiles and Competitive Analysis
7.1 Competitive Landscape
7.1.1 Competitive Benchmarking
7.1.2 LNG Market Share by Manufacturer (2024)
7.1.3 Industry BCG Matrix
7.1.4 Heat Map Analysis
7.1.5 Mergers and Acquisitions
7.2 QATAR PETROLEUM (QP) (QATAR)
7.2.1 Company Overview
7.2.2 Key Executives
7.2.3 Company Snapshot
7.2.4 Role of the Company in the Market
7.2.5 Sustainability and Social Responsibility
7.2.6 Operating Business Segments
7.2.7 Product Portfolio
7.2.8 Business Performance
7.2.9 Key Strategic Moves and Recent Developments
7.2.10 SWOT Analysis
7.3 ROYAL DUTCH SHELL (NETHERLANDS/UK)
7.4 EXXONMOBIL (USA)
7.5 CHEVRON (USA)
7.6 TOTALENERGIES (FRANCE)
7.7 BP (BRITISH PETROLEUM) (UK)
7.8 PETROCHINA (CHINA)
7.9 CNOOC (CHINA NATIONAL OFFSHORE OIL CORPORATION) (CHINA)
7.10 CHENIERE ENERGY (USA)
7.11 CONOCOPHILLIPS (USA)
7.12 PETRONAS (PETROLIAM NASIONAL BERHAD) (MALAYSIA)
7.13 GAZPROM (RUSSIA)
7.14 NOVATEK (RUSSIA)
7.15 ENI (ITALY)
7.16 REPSOL (SPAIN)
7.17 WOODSIDE PETROLEUM (AUSTRALIA)
7.18 SANTOS LIMITED (AUSTRALIA)
7.19 EQUINOR (FORMERLY STATOIL) (NORWAY)
7.20 SEMPRA ENERGY (USA)
7.21 KOGAS (KOREA GAS CORPORATION) (SOUTH KOREA)
7.22 MITSUBISHI CORPORATION (JAPAN)
7.23 MITSUI & COLTD. (JAPAN)
7.24 JERA (JAPAN)
7.25 INDIAN OIL CORPORATION (IOCL) (INDIA)
7.26 SONATRACH (ALGERIA)
Chapter 8: Global LNG Market By Region
8.1 Overview
8.2. North America LNG Market
8.2.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.2.2 Top Key Companies
8.2.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.2.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Nature
8.2.4.1 Odourless
8.2.4.2 Colourless
8.2.4.3 Non-Toxic
8.2.4.4 Non-Corrosive
8.2.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by LNG Infrastructure
8.2.5.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants
8.2.5.2 LNG Regasification Facilities
8.2.5.3 LNG Shipping
8.2.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Category
8.2.6.1 Transportation
8.2.6.2 Household
8.2.6.3 LNG Trucks
8.2.6.4 LNG Bus
8.2.6.5 Train
8.2.6.6 Trade
8.2.6.7 Maritime Application
8.2.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.2.7.1 US
8.2.7.2 Canada
8.2.7.3 Mexico
8.3. Eastern Europe LNG Market
8.3.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.3.2 Top Key Companies
8.3.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.3.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Nature
8.3.4.1 Odourless
8.3.4.2 Colourless
8.3.4.3 Non-Toxic
8.3.4.4 Non-Corrosive
8.3.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by LNG Infrastructure
8.3.5.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants
8.3.5.2 LNG Regasification Facilities
8.3.5.3 LNG Shipping
8.3.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Category
8.3.6.1 Transportation
8.3.6.2 Household
8.3.6.3 LNG Trucks
8.3.6.4 LNG Bus
8.3.6.5 Train
8.3.6.6 Trade
8.3.6.7 Maritime Application
8.3.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.3.7.1 Russia
8.3.7.2 Bulgaria
8.3.7.3 The Czech Republic
8.3.7.4 Hungary
8.3.7.5 Poland
8.3.7.6 Romania
8.3.7.7 Rest of Eastern Europe
8.4. Western Europe LNG Market
8.4.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.4.2 Top Key Companies
8.4.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.4.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Nature
8.4.4.1 Odourless
8.4.4.2 Colourless
8.4.4.3 Non-Toxic
8.4.4.4 Non-Corrosive
8.4.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by LNG Infrastructure
8.4.5.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants
8.4.5.2 LNG Regasification Facilities
8.4.5.3 LNG Shipping
8.4.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Category
8.4.6.1 Transportation
8.4.6.2 Household
8.4.6.3 LNG Trucks
8.4.6.4 LNG Bus
8.4.6.5 Train
8.4.6.6 Trade
8.4.6.7 Maritime Application
8.4.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.4.7.1 Germany
8.4.7.2 UK
8.4.7.3 France
8.4.7.4 The Netherlands
8.4.7.5 Italy
8.4.7.6 Spain
8.4.7.7 Rest of Western Europe
8.5. Asia Pacific LNG Market
8.5.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.5.2 Top Key Companies
8.5.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.5.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Nature
8.5.4.1 Odourless
8.5.4.2 Colourless
8.5.4.3 Non-Toxic
8.5.4.4 Non-Corrosive
8.5.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by LNG Infrastructure
8.5.5.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants
8.5.5.2 LNG Regasification Facilities
8.5.5.3 LNG Shipping
8.5.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Category
8.5.6.1 Transportation
8.5.6.2 Household
8.5.6.3 LNG Trucks
8.5.6.4 LNG Bus
8.5.6.5 Train
8.5.6.6 Trade
8.5.6.7 Maritime Application
8.5.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.5.7.1 China
8.5.7.2 India
8.5.7.3 Japan
8.5.7.4 South Korea
8.5.7.5 Malaysia
8.5.7.6 Thailand
8.5.7.7 Vietnam
8.5.7.8 The Philippines
8.5.7.9 Australia
8.5.7.10 New Zealand
8.5.7.11 Rest of APAC
8.6. Middle East & Africa LNG Market
8.6.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.6.2 Top Key Companies
8.6.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.6.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Nature
8.6.4.1 Odourless
8.6.4.2 Colourless
8.6.4.3 Non-Toxic
8.6.4.4 Non-Corrosive
8.6.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by LNG Infrastructure
8.6.5.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants
8.6.5.2 LNG Regasification Facilities
8.6.5.3 LNG Shipping
8.6.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Category
8.6.6.1 Transportation
8.6.6.2 Household
8.6.6.3 LNG Trucks
8.6.6.4 LNG Bus
8.6.6.5 Train
8.6.6.6 Trade
8.6.6.7 Maritime Application
8.6.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.6.7.1 Turkiye
8.6.7.2 Bahrain
8.6.7.3 Kuwait
8.6.7.4 Saudi Arabia
8.6.7.5 Qatar
8.6.7.6 UAE
8.6.7.7 Israel
8.6.7.8 South Africa
8.7. South America LNG Market
8.7.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.7.2 Top Key Companies
8.7.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.7.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Nature
8.7.4.1 Odourless
8.7.4.2 Colourless
8.7.4.3 Non-Toxic
8.7.4.4 Non-Corrosive
8.7.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by LNG Infrastructure
8.7.5.1 LNG Liquefaction Plants
8.7.5.2 LNG Regasification Facilities
8.7.5.3 LNG Shipping
8.7.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Category
8.7.6.1 Transportation
8.7.6.2 Household
8.7.6.3 LNG Trucks
8.7.6.4 LNG Bus
8.7.6.5 Train
8.7.6.6 Trade
8.7.6.7 Maritime Application
8.7.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.7.7.1 Brazil
8.7.7.2 Argentina
8.7.7.3 Rest of SA
Chapter 9 Analyst Viewpoint and Conclusion
9.1 Recommendations and Concluding Analysis
9.2 Potential Market Strategies
Chapter 10 Research Methodology
10.1 Research Process
10.2 Primary Research
10.3 Secondary Research
|
Global LNG Market |
|||
|
Base Year: |
2024 |
Forecast Period: |
2025-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2018-2023 |
Market Size In 2024: |
USD 146.84 Billion |
|
Forecast Period 2024-32 CAGR: |
8.6% |
Market Size In 2032: |
USD 284.10 Billion |
|
Segments Covered: |
By Nature |
|
|
|
By LNG Infrastructure |
|
||
|
By Category |
|
||
|
By Region |
|
||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
|
||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
|
||
|
Key Opportunities: |
|
||
|
Companies Covered in The Report: |
|
||













