Seeds Market Synopsis
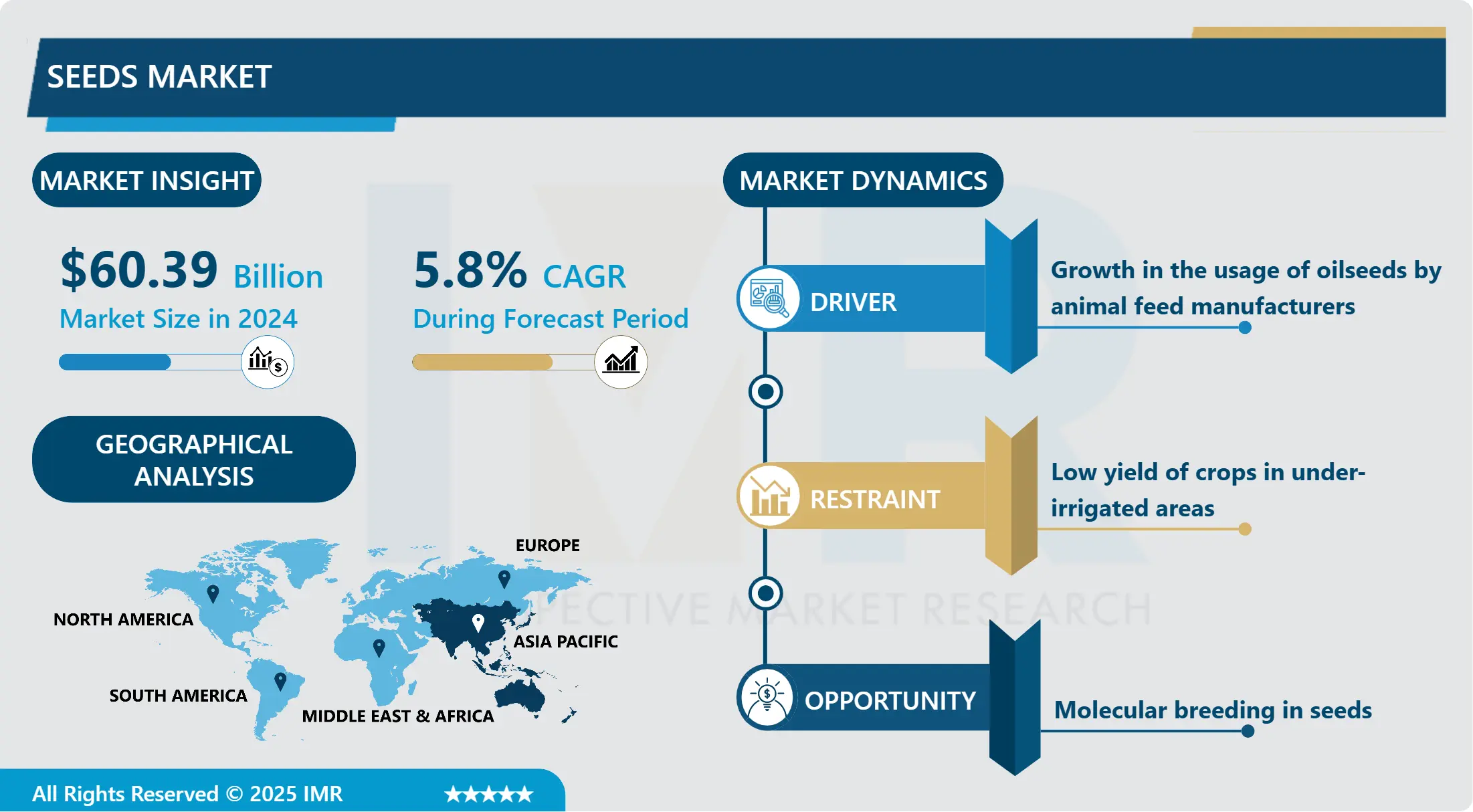
Seeds Market Size Was Valued at USD 60.39 Billion in 2024, and is Projected to Reach USD 94.81 Billion by 2032, Growing at a CAGR of 5.80% From 2025-2032.
The worldwide commerce and production of seeds used to grow fruits, vegetables, crops, and other plants is included in the seeds market. There are many different kinds of seeds available in this market, including conventional, organic, and genetically modified (GM) seeds. Field crops, horticulture crops, and feed crops are important market categories for seeds. Government laws, increased awareness of sustainable farming practices, high-yield and disease-resistant crop demand, and advances in agricultural biotechnology all impact the market dynamics. Furthermore, the seeds market is an essential part of the global agriculture business since it contributes significantly to economic growth, environmental sustainability, and food security.
The growing worldwide population is driving up food consumption, which is fueling the market for seeds. The demand for premium seeds has increased significantly as sustainable agriculture and food security get more and more attention. The industry is expanding mostly due to advances in seed technology, such as hybrid and genetically modified (GM) seeds. By improving agricultural productivity, resilience to pests and diseases, and tolerance to unfavorable climatic circumstances, these technical advancements help to more efficiently supply the world's food need.
In addition, the market for seeds is being supported by government efforts and advantageous agricultural policies in different regions. Farmers are being encouraged to adopt better seed types by means of subsidies, incentives, and expenditures in agricultural research and development. The Asia-Pacific area is becoming a significant market for seeds due to its large amount of arable land and growing use of contemporary farming methods. The market for organic seeds is also being driven by the expanding popularity of organic farming and the growing inclination of consumers toward organic food items.
The industry does, however, confront obstacles including strict laws governing genetically modified crops and the high price of hybrid and GM seeds, which can be prohibitive for small-scale growers. Significant obstacles are also presented by the environmental issues raised by the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers on these seeds. Despite these obstacles, there is a lot of room for development in the seeds market because to ongoing advancements in seed technology and rising agricultural infrastructure spending. In the upcoming years, the market is expected to rise significantly due to increased worldwide attention being paid to food security and sustainable agriculture methods.

Seeds Market Trend Analysis
Seeds Market Growth Driver- Growing Acceptance and Technological Advancements in Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) in the Seeds Market
- The market for seeds is seeing a marked change in favor of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which will increase agricultural production and sustainability. Herbicide tolerance and insect resistance are two examples of the beneficial features that genetically modified seeds are engineered to have. This increases the resistance of crops to herbicides that might otherwise damage them, improving weed control and lowering the need for repeated herbicide treatments. Furthermore, to reduce agricultural losses from insect damage, insect-resistant genetically modified seeds generate proteins that are harmful to some pests but safe for humans and other non-target creatures. In addition to increasing yields, this technical development has reduced the need for chemical pesticides, supporting ecologically friendly agricultural methods.
- Several nations, like the US, Brazil, and Argentina, have been in the forefront of GM crop adoption, capitalizing on the advantages to increase agricultural productivity. The extensive application of genetically modified seeds in these nations has shown the possibility for improved agricultural yields, which would benefit farmers financially and promote food security. Global acceptability of GM technology, however, differs by location, with some confronting governmental obstacles and mistrust from consumers. For example, the adoption of GMOs has stalled in Europe due to strict laws and public worries about the safety and ethical implications of GMOs. Notwithstanding these obstacles, progress in biotechnology, especially with regard to gene editing instruments such as CRISPR, is opening the door to more accurate and focused genetic alterations. With the use of these instruments, scientists may add desired features without inserting foreign DNA, which may allay some of the worries related to conventional GMOs. It is anticipated that the adoption and use of genetically modified seeds will increase as research and regulatory frameworks change, spurring more innovation and market expansion for seeds.
Seeds Market Expansion Opportunity- Increasing Focus on Sustainable and Organic Farming Practices in the Seeds Market
- The seeds market is the increasing focus on sustainable and organic farming practices, driven by a rising wave of health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers. This shift in consumer preferences is fueling demand for organic and non-GMO seeds, as people seek food products that are free from synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. In response, seed companies are expanding their portfolios to include a wider variety of organic seeds, which are cultivated using natural methods without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. These companies are not only developing seeds that cater to the growing organic segment but are also investing in research to enhance the quality and yield of organic crops. This trend towards organic farming is also supported by the growing awareness of the environmental benefits of reduced chemical use, such as improved soil health, biodiversity conservation, and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- The movement towards sustainable agriculture is further bolstered by favorable government policies and incentives aimed at promoting eco-friendly farming practices. Various governments around the world are implementing programs and subsidies to encourage farmers to adopt sustainable methods, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage. These practices help maintain soil fertility, reduce erosion, and enhance water retention, contributing to long-term agricultural sustainability. Additionally, seed companies are aligning with global sustainability goals by investing in sustainable packaging solutions and adopting eco-friendly practices throughout their supply chains. For instance, some companies are exploring biodegradable and recyclable packaging materials to reduce their environmental footprint. As sustainability continues to gain prominence, the organic seeds market is expected to grow, driven by consumer demand, supportive policies, and the commitment of companies to integrate sustainability into their core operations.
Seeds Market Segment Analysis:
Seeds Market Segmented based on into Type, Crop Type, Trait, and Region.
By Type, Genetically Modified segment is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period
- Genetically modified (GM) crops have revolutionized agriculture by incorporating traits like herbicide tolerance and insect resistance, addressing significant challenges faced by farmers worldwide. Herbicide-tolerant GM crops, such as soybean, corn, and cotton, have been engineered to withstand specific herbicides, allowing farmers to apply these chemicals without harming the crop itself. This trait enables more efficient weed management, reducing the need for labor-intensive manual weeding and minimizing herbicide application costs. As a result, farmers can achieve higher yields per acre while maintaining soil health through reduced tillage practices, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Insect-resistant GM crops, exemplified by Bt cotton and Bt corn, express proteins derived from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) that are toxic to certain insect pests. These crops provide built-in protection against pests like bollworms and corn borers, which can devastate yields if left unchecked. By reducing the need for chemical insecticides, Bt crops contribute to environmental sustainability and human health by minimizing pesticide exposure risks for farmers and consumers alike. This technology has been particularly beneficial in regions where pest pressure is high, enabling more reliable crop production and enhancing food security.
- Overall, GM crops with herbicide tolerance and insect resistance traits have become integral tools for modern agriculture, offering farmers practical solutions to challenges like weed control and pest management. Their widespread adoption underscores their effectiveness in increasing agricultural productivity, improving farm economics, and promoting sustainable farming practices globally. As research and development continue to advance, future GM crop innovations hold promise for addressing emerging agricultural issues and meeting the growing global demand for food in a changing climate.
By Trait, Herbicide tolerance segment held the largest share in 2024
- A crucial characteristic of genetically modified (GM) crops is herbicide tolerance, which enables farmers to control weeds with targeted herbicides that destroy undesirable plants without endangering the crop. Given that weed competition can negatively affect crop yields in modern agriculture, this skill is very beneficial. Soybean, corn, and cotton genetically modified (GM) to confer herbicide resistance (glyphosate, or Roundup), allowing farmers to implement reduced- or no-till farming techniques. By using these techniques, soil structure and organic matter are preserved and there is less disturbance of the soil during planting and subsequent crop management. Consequently, no-till farming is a sustainable option for preserving agricultural output while minimizing environmental effect since it preserves soil moisture, lowers erosion, and improves soil health over time.
- GM crops that include insect resistance features, particularly those resulting from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) technology, have revolutionized agricultural pest control practices. Bt crops naturally repel some insect pests like cotton bollworms and corn borers by producing proteins that are harmful to them. Bt technology provides a focused and ecologically benign method of pest management by lowering dependency on chemical pesticides, which can have negative impacts on beneficial creatures and human health. This invention is particularly useful in areas with strong insect pressure and low efficacy of conventional pest control techniques. Increased crop yields and lower input costs benefit farmers, while food items with perhaps fewer pesticide residues benefit consumers, helping to meet goals for sustainability and food safety.
- The ongoing research and development of genetically modified crops with insect and herbicide resistance highlights their significance in the contemporary agricultural industry's pursuit of efficient and sustainable food production systems. Future GM crop inventions may improve these qualities even more as research progresses, providing fresh approaches to new agricultural problems and satisfying the demands of global food security in a changing environment.
Seeds Market Regional Insights:
Asia Pacific's is Expected to Dominate the Market Over the Forecast period
- Asia Pacific's vast population and varied farming methods are driving a major transition in the region's seeds business. Key participants include nations like China and India, which have large amounts of arable land and long histories of agriculture. Modern agricultural technology and traditional farming practices coexist, which causes a slow transition to hybrid seeds that provide greater yields and improved resistance to pests and diseases. The use of hybrid seeds is essential to supplying the increasing demand for food in the face of declining agricultural land and shifting weather patterns.
- Governmental activities are a major factor in determining the characteristics of the Asia Pacific seeds industry. Modern farm infrastructure and policies to improve food security are major forces behind market expansion. To increase agricultural production, programs like India's National Food Security Mission (NFSM) and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) encourage the use of hybrid seeds and high-yielding varieties (HYVs). In a similar vein, China's agriculture policies prioritize technological transfer and innovation to boost crop yields and encourage sustainable farming methods. The favorable climate created by these rules and investments encourages seed firms to develop, diversify their product lines, and meet the wide range of agricultural demands in the area.
Active Key Players in the Seeds Market
- Bayer AG (Germany)
- Syngenta Crop Protection AG (Switzerland)
- KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA (Germany)
- Corteva (US)
- Limagrain (France)
- Advanta Seeds (India)
- Sakata Seed Corporation (Japan)
- DLF Seeds A/S (Denmark)
- Enza Zaden Beheer B.V. (Netherlands)
- Rallis India Limited (India)
- FMC Corporation (US)
- TAKII & CO.,LTD. (Japan)
- Royal Barenbrug Group (Netherlands)
- Longping High-Tech (China)
- Other Active Players
Key Industry Developments in the Seeds Market:
- In April 2023, Bayer revealed an investment of overall 60 million euros from 2023 onwards in its corn seed production facility in Pochuiky, Ukraine. With this, the life sciences company emphasizes its commitment to Ukraine and strengthens its Crop Science business in the country, contributing to rebuilding the economy.
- In February 2023, Corteva launched ‘Optimum GLY Conala.’ It is an advanced herbicide-tolerant trait technology for canola farmers. Optimum GLY canola will be offered for commercial planting in Canada and the United States through Corteva Agriscience seed brands Pioneer and Brevant seeds.
|
Global Seeds Market |
|||
|
Base Year: |
2024 |
Forecast Period: |
2025-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2018 to 2023 |
Market Size in 2024: |
USD 60.39 Bn. |
|
Forecast Period 2025-32 CAGR: |
5.80% |
Market Size in 2032: |
USD 94.81 Bn. |
|
Segments Covered: |
By Type |
|
|
|
By Crop Type |
|
||
|
By Trait |
|
||
|
By Region |
|
||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
|
||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
|
||
|
Key Opportunities: |
|
||
|
Companies Covered in the report: |
|
||
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Scope and Coverage
Chapter 2:Executive Summary
Chapter 3: Market Landscape
3.1 Market Dynamics
3.1.1 Drivers
3.1.2 Restraints
3.1.3 Opportunities
3.1.4 Challenges
3.2 Market Trend Analysis
3.3 PESTLE Analysis
3.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
3.5 Industry Value Chain Analysis
3.6 Ecosystem
3.7 Regulatory Landscape
3.8 Price Trend Analysis
3.9 Patent Analysis
3.10 Technology Evolution
3.11 Investment Pockets
3.12 Import-Export Analysis
Chapter 4: Seeds Market by Type (2018-2032)
4.1 Seeds Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
4.2 Market Overview
4.3 Genetically Modified
4.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
4.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
4.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
4.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
4.4 Conventional
Chapter 5: Seeds Market by Crop Type (2018-2032)
5.1 Seeds Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
5.2 Market Overview
5.3 Cereals & grains
5.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
5.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
5.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
5.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
5.4 Corn
5.5 Wheat
5.6 Rice
5.7 Other cereals & grains
5.8 Oilseeds & pulses
5.9 Soybean
5.10 Canola
5.11 Cotton
5.12 Other oilseeds & pulses
5.13 Fruits & vegetables
5.14 Solanaceae
5.15 Cucurbits
5.16 Brassicas
5.17 Leafy vegetables
5.18 Roots & bulbs
5.19 Other fruits & vegetables
5.20 Other crop types
Chapter 6: Seeds Market by Trait (2018-2032)
6.1 Seeds Market Snapshot and Growth Engine
6.2 Market Overview
6.3 Herbicide tolerance
6.3.1 Introduction and Market Overview
6.3.2 Historic and Forecasted Market Size in Value USD and Volume Units
6.3.3 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors, and Opportunities
6.3.4 Geographic Segmentation Analysis
6.4 Insect resistance
6.5 Other traits
Chapter 7: Company Profiles and Competitive Analysis
7.1 Competitive Landscape
7.1.1 Competitive Benchmarking
7.1.2 Seeds Market Share by Manufacturer (2024)
7.1.3 Industry BCG Matrix
7.1.4 Heat Map Analysis
7.1.5 Mergers and Acquisitions
7.2 BAYER AG (GERMANY)
7.2.1 Company Overview
7.2.2 Key Executives
7.2.3 Company Snapshot
7.2.4 Role of the Company in the Market
7.2.5 Sustainability and Social Responsibility
7.2.6 Operating Business Segments
7.2.7 Product Portfolio
7.2.8 Business Performance
7.2.9 Key Strategic Moves and Recent Developments
7.2.10 SWOT Analysis
7.3 SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG (SWITZERLAND)
7.4 KWS SAAT SE & CO. KGAA (GERMANY)
7.5 CORTEVA (US)
7.6 LIMAGRAIN (FRANCE)
7.7 ADVANTA SEEDS (INDIA)
7.8 SAKATA SEED CORPORATION (JAPAN)
7.9 DLF SEEDS A/S (DENMARK)
7.10 ENZA ZADEN BEHEER B.V. (NETHERLANDS)
7.11 RALLIS INDIA LIMITED (INDIA)
7.12 FMC CORPORATION (US)
7.13 TAKII & CO. LTD. (JAPAN)
7.14 ROYAL BARENBRUG GROUP (NETHERLANDS)
7.15 LONGPING HIGH-TECH (CHINA)
Chapter 8: Global Seeds Market By Region
8.1 Overview
8.2. North America Seeds Market
8.2.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.2.2 Top Key Companies
8.2.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.2.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Type
8.2.4.1 Genetically Modified
8.2.4.2 Conventional
8.2.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Crop Type
8.2.5.1 Cereals & grains
8.2.5.2 Corn
8.2.5.3 Wheat
8.2.5.4 Rice
8.2.5.5 Other cereals & grains
8.2.5.6 Oilseeds & pulses
8.2.5.7 Soybean
8.2.5.8 Canola
8.2.5.9 Cotton
8.2.5.10 Other oilseeds & pulses
8.2.5.11 Fruits & vegetables
8.2.5.12 Solanaceae
8.2.5.13 Cucurbits
8.2.5.14 Brassicas
8.2.5.15 Leafy vegetables
8.2.5.16 Roots & bulbs
8.2.5.17 Other fruits & vegetables
8.2.5.18 Other crop types
8.2.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Trait
8.2.6.1 Herbicide tolerance
8.2.6.2 Insect resistance
8.2.6.3 Other traits
8.2.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.2.7.1 US
8.2.7.2 Canada
8.2.7.3 Mexico
8.3. Eastern Europe Seeds Market
8.3.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.3.2 Top Key Companies
8.3.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.3.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Type
8.3.4.1 Genetically Modified
8.3.4.2 Conventional
8.3.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Crop Type
8.3.5.1 Cereals & grains
8.3.5.2 Corn
8.3.5.3 Wheat
8.3.5.4 Rice
8.3.5.5 Other cereals & grains
8.3.5.6 Oilseeds & pulses
8.3.5.7 Soybean
8.3.5.8 Canola
8.3.5.9 Cotton
8.3.5.10 Other oilseeds & pulses
8.3.5.11 Fruits & vegetables
8.3.5.12 Solanaceae
8.3.5.13 Cucurbits
8.3.5.14 Brassicas
8.3.5.15 Leafy vegetables
8.3.5.16 Roots & bulbs
8.3.5.17 Other fruits & vegetables
8.3.5.18 Other crop types
8.3.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Trait
8.3.6.1 Herbicide tolerance
8.3.6.2 Insect resistance
8.3.6.3 Other traits
8.3.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.3.7.1 Russia
8.3.7.2 Bulgaria
8.3.7.3 The Czech Republic
8.3.7.4 Hungary
8.3.7.5 Poland
8.3.7.6 Romania
8.3.7.7 Rest of Eastern Europe
8.4. Western Europe Seeds Market
8.4.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.4.2 Top Key Companies
8.4.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.4.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Type
8.4.4.1 Genetically Modified
8.4.4.2 Conventional
8.4.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Crop Type
8.4.5.1 Cereals & grains
8.4.5.2 Corn
8.4.5.3 Wheat
8.4.5.4 Rice
8.4.5.5 Other cereals & grains
8.4.5.6 Oilseeds & pulses
8.4.5.7 Soybean
8.4.5.8 Canola
8.4.5.9 Cotton
8.4.5.10 Other oilseeds & pulses
8.4.5.11 Fruits & vegetables
8.4.5.12 Solanaceae
8.4.5.13 Cucurbits
8.4.5.14 Brassicas
8.4.5.15 Leafy vegetables
8.4.5.16 Roots & bulbs
8.4.5.17 Other fruits & vegetables
8.4.5.18 Other crop types
8.4.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Trait
8.4.6.1 Herbicide tolerance
8.4.6.2 Insect resistance
8.4.6.3 Other traits
8.4.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.4.7.1 Germany
8.4.7.2 UK
8.4.7.3 France
8.4.7.4 The Netherlands
8.4.7.5 Italy
8.4.7.6 Spain
8.4.7.7 Rest of Western Europe
8.5. Asia Pacific Seeds Market
8.5.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.5.2 Top Key Companies
8.5.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.5.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Type
8.5.4.1 Genetically Modified
8.5.4.2 Conventional
8.5.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Crop Type
8.5.5.1 Cereals & grains
8.5.5.2 Corn
8.5.5.3 Wheat
8.5.5.4 Rice
8.5.5.5 Other cereals & grains
8.5.5.6 Oilseeds & pulses
8.5.5.7 Soybean
8.5.5.8 Canola
8.5.5.9 Cotton
8.5.5.10 Other oilseeds & pulses
8.5.5.11 Fruits & vegetables
8.5.5.12 Solanaceae
8.5.5.13 Cucurbits
8.5.5.14 Brassicas
8.5.5.15 Leafy vegetables
8.5.5.16 Roots & bulbs
8.5.5.17 Other fruits & vegetables
8.5.5.18 Other crop types
8.5.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Trait
8.5.6.1 Herbicide tolerance
8.5.6.2 Insect resistance
8.5.6.3 Other traits
8.5.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.5.7.1 China
8.5.7.2 India
8.5.7.3 Japan
8.5.7.4 South Korea
8.5.7.5 Malaysia
8.5.7.6 Thailand
8.5.7.7 Vietnam
8.5.7.8 The Philippines
8.5.7.9 Australia
8.5.7.10 New Zealand
8.5.7.11 Rest of APAC
8.6. Middle East & Africa Seeds Market
8.6.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.6.2 Top Key Companies
8.6.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.6.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Type
8.6.4.1 Genetically Modified
8.6.4.2 Conventional
8.6.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Crop Type
8.6.5.1 Cereals & grains
8.6.5.2 Corn
8.6.5.3 Wheat
8.6.5.4 Rice
8.6.5.5 Other cereals & grains
8.6.5.6 Oilseeds & pulses
8.6.5.7 Soybean
8.6.5.8 Canola
8.6.5.9 Cotton
8.6.5.10 Other oilseeds & pulses
8.6.5.11 Fruits & vegetables
8.6.5.12 Solanaceae
8.6.5.13 Cucurbits
8.6.5.14 Brassicas
8.6.5.15 Leafy vegetables
8.6.5.16 Roots & bulbs
8.6.5.17 Other fruits & vegetables
8.6.5.18 Other crop types
8.6.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Trait
8.6.6.1 Herbicide tolerance
8.6.6.2 Insect resistance
8.6.6.3 Other traits
8.6.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.6.7.1 Turkiye
8.6.7.2 Bahrain
8.6.7.3 Kuwait
8.6.7.4 Saudi Arabia
8.6.7.5 Qatar
8.6.7.6 UAE
8.6.7.7 Israel
8.6.7.8 South Africa
8.7. South America Seeds Market
8.7.1 Key Market Trends, Growth Factors and Opportunities
8.7.2 Top Key Companies
8.7.3 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Segments
8.7.4 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Type
8.7.4.1 Genetically Modified
8.7.4.2 Conventional
8.7.5 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Crop Type
8.7.5.1 Cereals & grains
8.7.5.2 Corn
8.7.5.3 Wheat
8.7.5.4 Rice
8.7.5.5 Other cereals & grains
8.7.5.6 Oilseeds & pulses
8.7.5.7 Soybean
8.7.5.8 Canola
8.7.5.9 Cotton
8.7.5.10 Other oilseeds & pulses
8.7.5.11 Fruits & vegetables
8.7.5.12 Solanaceae
8.7.5.13 Cucurbits
8.7.5.14 Brassicas
8.7.5.15 Leafy vegetables
8.7.5.16 Roots & bulbs
8.7.5.17 Other fruits & vegetables
8.7.5.18 Other crop types
8.7.6 Historic and Forecasted Market Size by Trait
8.7.6.1 Herbicide tolerance
8.7.6.2 Insect resistance
8.7.6.3 Other traits
8.7.7 Historic and Forecast Market Size by Country
8.7.7.1 Brazil
8.7.7.2 Argentina
8.7.7.3 Rest of SA
Chapter 9 Analyst Viewpoint and Conclusion
9.1 Recommendations and Concluding Analysis
9.2 Potential Market Strategies
Chapter 10 Research Methodology
10.1 Research Process
10.2 Primary Research
10.3 Secondary Research
|
Global Seeds Market |
|||
|
Base Year: |
2024 |
Forecast Period: |
2025-2032 |
|
Historical Data: |
2018 to 2023 |
Market Size in 2024: |
USD 60.39 Bn. |
|
Forecast Period 2025-32 CAGR: |
5.80% |
Market Size in 2032: |
USD 94.81 Bn. |
|
Segments Covered: |
By Type |
|
|
|
By Crop Type |
|
||
|
By Trait |
|
||
|
By Region |
|
||
|
Key Market Drivers: |
|
||
|
Key Market Restraints: |
|
||
|
Key Opportunities: |
|
||
|
Companies Covered in the report: |
|
||













